We all love indulging in a decadent dessert or sipping on a sweet drink—but what if your sugar habit is doing more than just adding inches to your waistline? Emerging research suggests that too much sugar doesn’t just affect your weight; it could be aging your skin faster, causing breakouts, and even contributing to dullness and wrinkles.
The culprit? A natural process called glycation, where excess sugar molecules attach to collagen and elastin—the proteins that keep your skin firm and youthful. Over time, this leads to sagging skin, fine lines, and inflammation, making you look older than you are. Let’s explore how sugar impacts skin health.
How Sugar Affects Your Skin
1. Accelerates Aging
Sugar speeds up skin aging through glycation—a process where sugar molecules attach to collagen and elastin. These proteins keep skin firm and youthful. Glycation damages them, causing wrinkles and sagging. A study in Clinics in Dermatology found high-sugar diets increase advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which age skin faster. This means that too much sugar can leave your skin looking older.
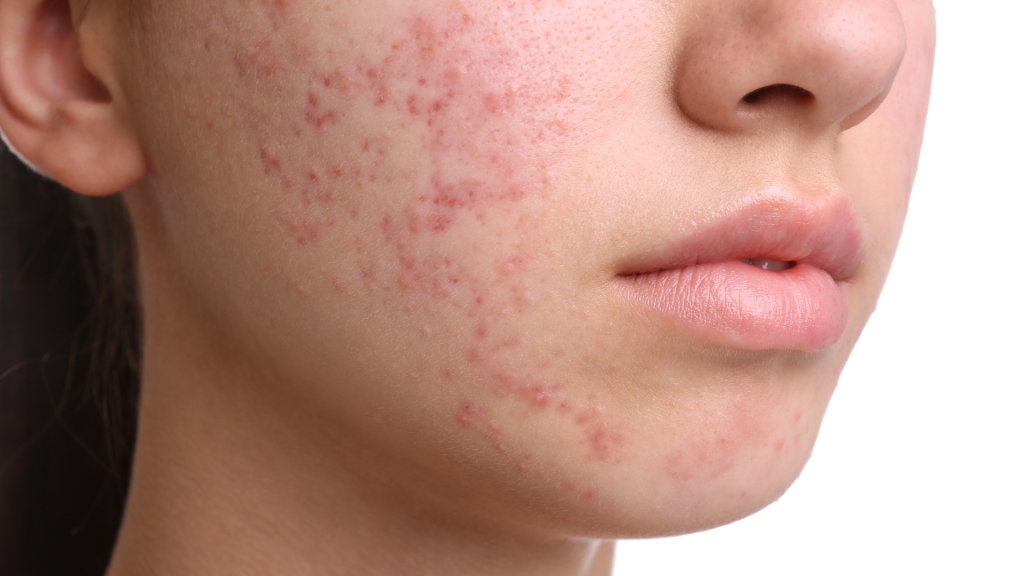
2. Promotes Acne
Sugar worsens acne by spiking insulin, increasing oil production. Excess oil clogs pores, causing breakouts. A JAMA Dermatology study linked sugary and fatty foods to acne, especially in teens. Sugar also fuels inflammation, making skin red and irritated. Next time you crave sweets, remember—your skin may pay the price.
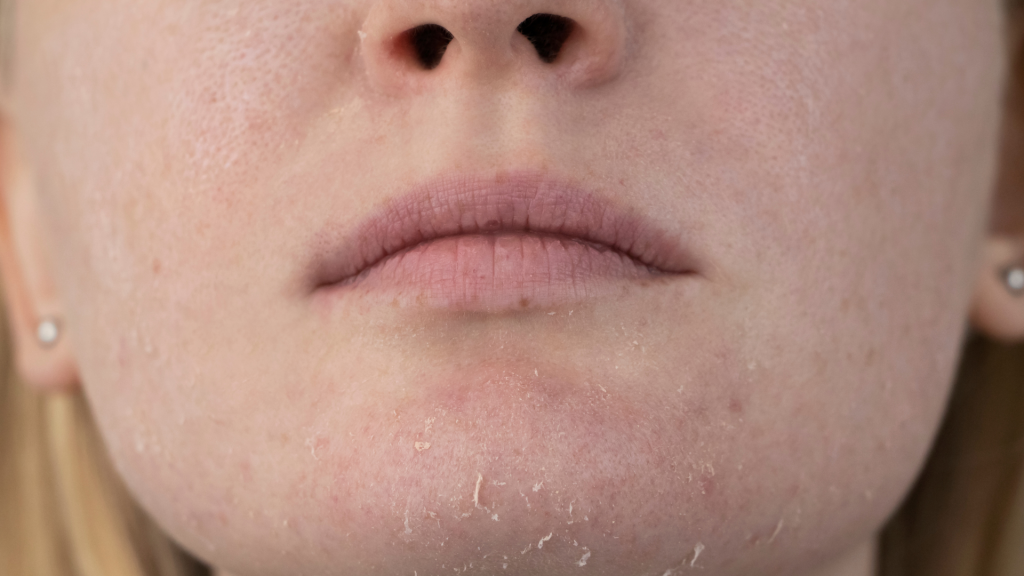
3. Damages Collagen & Elastin
Sugar also harms collagen and elastin—key proteins for firm, youthful skin. Excess sugar binds to these fibers, weakening them over time. This leads to wrinkles, sagging, and dryness. The more sugar you eat, the faster your skin may age.
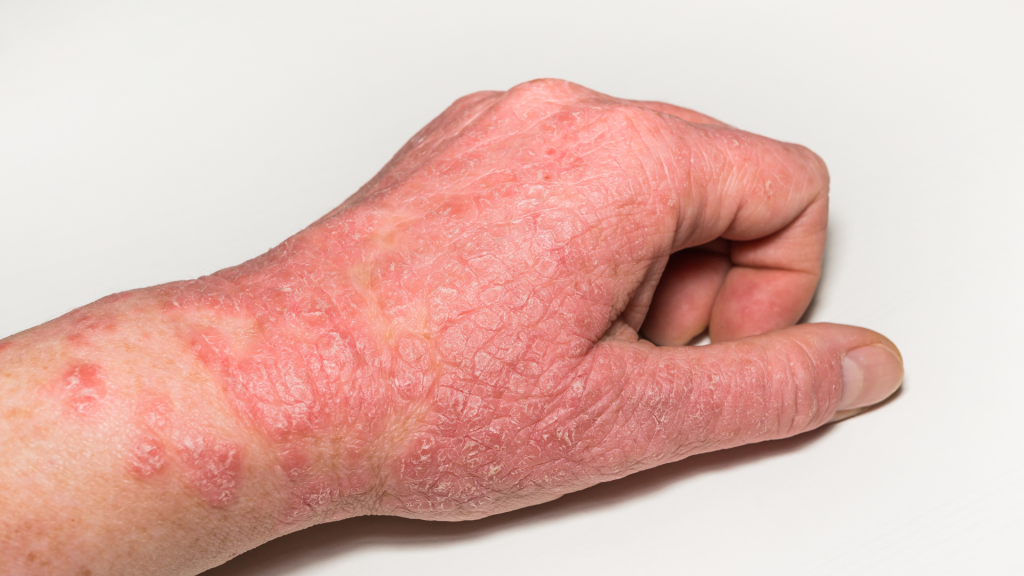
4. Worsens Psoriasis
Did you know your sweet tooth could be aggravating psoriasis? This autoimmune condition, which causes red, scaly skin patches, may flare up due to sugar’s inflammatory effects. Research suggests that excessive sugar intake can trigger or worsen symptoms by increasing inflammation in the body. For the millions of adults living with psoriasis worldwide, reducing sugar consumption could be a simple yet effective way to help manage flare-ups and support healthier skin.
5. Inflammation: Sugar’s Silent Attack on Skin
Eating too much sugar sparks inflammation in your body. Here’s why: Sugar spikes insulin levels, which boosts androgen (male hormone) production. These hormones ramp up oil production in your skin, clogging pores and triggering acne. But the damage doesn’t stop there. Chronic inflammation also slows your skin’s natural repair process, leaving it defenseless against premature aging.
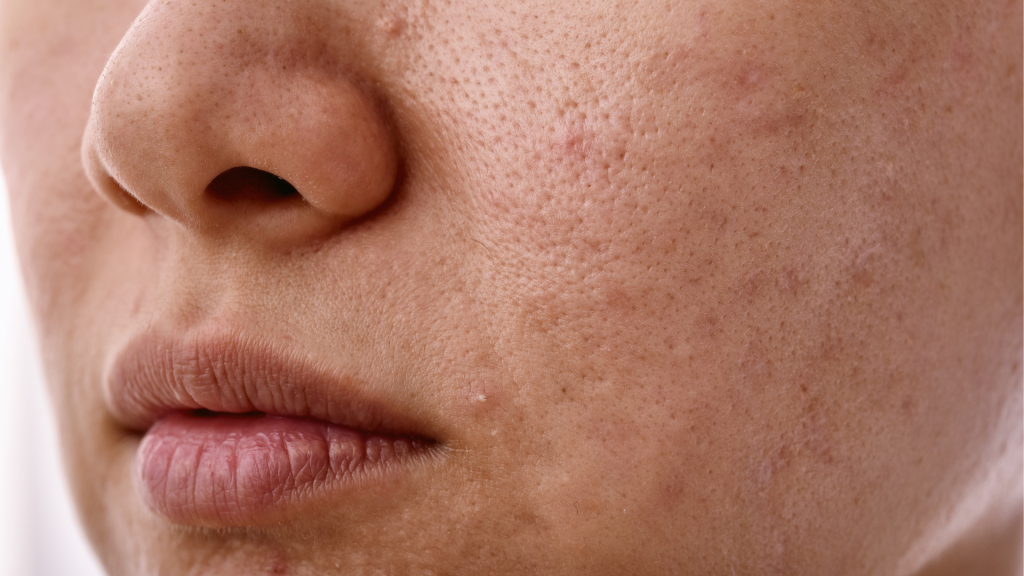
6. Glycation: How Sugar Steals Your Youth
Glycation occurs when sugar molecules latch onto collagen and elastin—the proteins responsible for keeping skin plump and firm. This creates harmful compounds called AGEs (advanced glycation end products), which break down these essential proteins. The result? Loss of elasticity, deeper wrinkles, and sagging skin. Bottom line: The more sugar you consume, the faster your skin shows signs of aging.
Tips to Help Reduce Your Sugar Intake
1. Watch Out for Hidden Sugars
From white bread and flavored yogurt to sauces and frozen meals – secretly pack more sugar than you’d expect, causing blood sugar spikes that accelerate skin aging through glycation. These processed foods and refined carbs break down quickly into sugar, damaging collagen over time. Simple swaps like choosing sprouted grain bread, plain yogurt with berries, homemade sauces, and nuts instead of sugary protein bars can help stabilize blood sugar levels and protect your skin. And You’ll not only reduce glycation’s aging effects but also gain better control over what you’re actually putting into your body.
2. Use Collagen-Boosting Skincare Ingredients
The right skincare ingredients—like Vitamin C, retinol, niacinamide, peptides, and green tea extract—work at a cellular level to boost collagen, fight oxidative stress, and prevent sugar-related damage. By strengthening your skin’s natural defenses and repair processes, they help maintain firmness, smoothness, and resilience over time, counteracting the effects of glycation and aging.
3. Choose Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Sugar and environmental factors create free radicals that damage collagen, but antioxidants fight back. Specifically, vitamin-rich foods like berries, citrus, and leafy greens neutralize these harmful molecules. Additionally, they provide nutrients that boost collagen production, maintaining skin’s firmness. Over time, a diet high in antioxidants helps prevent premature aging, reduces oxidative stress, and promotes a healthy, glowing complexion. For best results, pair these foods with sun protection and proper hydration.

4. Try Skin-Friendly Treats for Sweet Cravings
Instead of sugar-laden treats, opt for skin-friendly alternatives. First, dark chocolate makes an excellent choice—it’s lower in sugar than most desserts and rich in antioxidants that fight glycation. Additionally, nut butters like almond or walnut butter provide healthy fats and vitamin E, which protect skin elasticity and hydration. However, always choose natural or homemade versions to avoid added sugars. For example, my go-to homemade chocolate protein cookies satisfy cravings without the sugar overload. Ultimately, these swaps let you indulge wisely while keeping your skin glowing.
5. Adopt Healthy, Collagen-Supporting Habits
First, regular exercise improves blood flow, nourishing skin cells and boosting collagen production. At the same time, it helps control blood sugar, reducing glycation damage. Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial. Water maintains skin elasticity and promotes cell renewal, both of which help preserve collagen. Finally, quality sleep matters greatly. During rest, your skin repairs itself and removes sugar-related toxins. Getting 7-8 hours nightly allows for proper collagen regeneration, leading to firmer, healthier skin over time.
6. Incorporate Fermented Foods
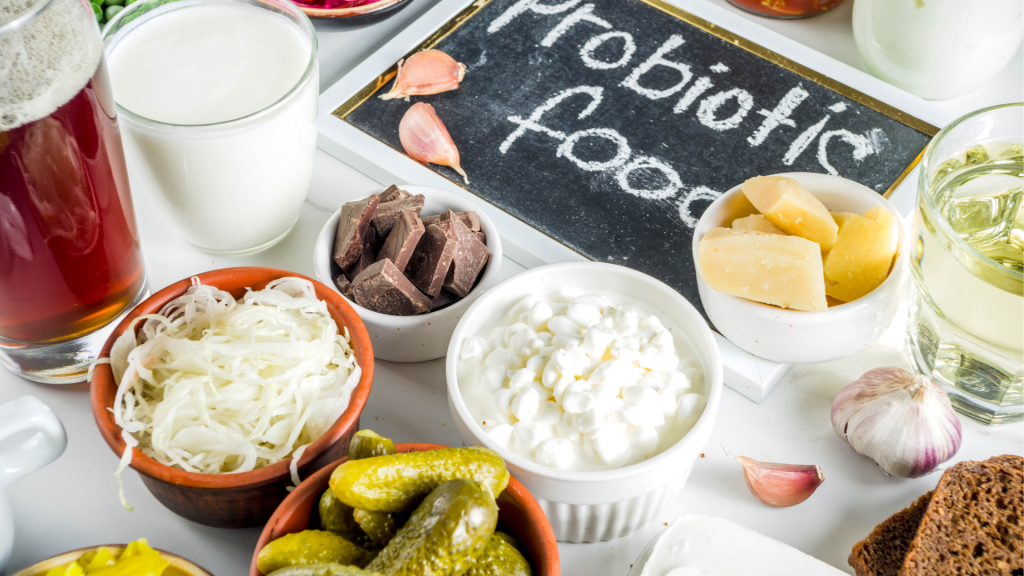

Fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut work wonders for your skin—but how? First, their probiotics boost gut health, creating a balanced microbiome. As a result, this reduces body-wide inflammation that often stems from sugar consumption. Consequently, your skin benefits with less redness, fewer breakouts, and slowed aging. Ultimately, a healthy gut helps your skin resist sugar’s damaging effects naturally.