Overview
What is GERD?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation. While occasional acid reflux is common, GERD is diagnosed when reflux occurs at least twice a week for several weeks. Unlike temporary reflux, GERD results from a malfunction in the esophageal barrier. It affects about 20% of adults and 10% of children in the U.S., with symptoms often managed through lifestyle changes, medications, or, in rare cases, surgery.
What is Acid Reflux?
Normally, stomach acid should move downward during digestion. But when it flows backward into the esophagus and throat, it causes acid reflux—leading to irritation and inflammation. Most people occasionally experience this as heartburn (burning chest pain) or indigestion (stomach discomfort after eating).
While occasional reflux is harmless, frequent episodes can develop into GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease). Chronic acid reflux not only disrupts daily life but can also damage the esophagus over time. Proper management is key to preventing long-term complications.
Symptoms
GERD (chronic acid reflux) causes uncomfortable symptoms when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. The most common signs include:
- Heartburn: A burning chest pain, often after eating or at night.
- Regurgitation: Sour-tasting fluid or food coming back up into the throat.
- Chest/upper abdominal pain: Discomfort that may feel like indigestion.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): A sensation of food sticking in the throat.
- Globus sensation: The feeling of a persistent lump in the throat.
Nighttime GERD can also trigger:
- Chronic coughing
- Hoarseness or laryngitis (vocal cord irritation)
- Asthma flare-ups or new breathing issues
If these symptoms occur frequently (twice a week or more), it could indicate GERD and may require medical attention to prevent complications.
Can GERD affect Newborns?
GERD in Babies: More Than Just Spit-Up
While occasional spit-up is normal for infants, GERD is a more serious condition that can interfere with feeding and cause discomfort. Unlike simple regurgitation, GERD involves problematic acid reflux that distresses the baby or leads to complications.
Which Babies Are at Higher Risk?
Premature infants and those with esophageal abnormalities are more prone to GERD. Pediatricians typically investigate GERD when feeding difficulties or other concerning symptoms appear.
Warning Signs of GERD in Infants & Toddlers:
- Unusual irritability or constant fussiness
- Feeding refusal or apparent discomfort during meals
- Frequent small vomits (beyond typical spit-up)
- Sleep disturbances due to discomfort
- Respiratory symptoms like wheezing or a hoarse cry
- Persistent sour milk breath
Diagnosis
GERD is often diagnosed based on symptoms like frequent heartburn and regurgitation. However, if symptoms are severe or don’t improve with treatment, your doctor may recommend further testing:
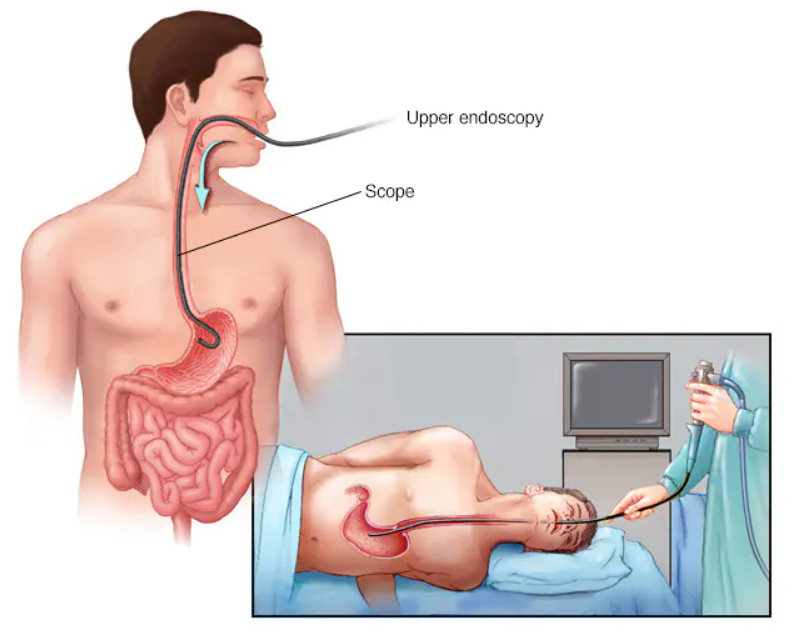
1. Upper Endoscopy (EGD)
- A thin, flexible tube with a camera is passed down your throat to examine the esophagus and stomach.
- Can detect esophagitis (inflammation), ulcers, or Barrett’s esophagus (a precancerous condition).
- A biopsy (small tissue sample) may be taken for further testing.
- If the esophagus is narrowed, it can be stretched (dilated) during the procedure.
2. Ambulatory Acid (pH) Monitoring
- Measures how often and for how long stomach acid enters the esophagus.
- A small catheter (tube) is inserted through the nose into the esophagus, or a wireless capsule is placed during an endoscopy.
- The device records acid levels over 24–48 hours while you eat and sleep normally.
3. Barium Swallow (X-ray of the Upper Digestive Tract)
- You drink a chalky liquid (barium) that coats the esophagus and stomach, making them visible on X-rays.
- Helps detect narrowing (strictures), hiatal hernias, or swallowing problems.
- Sometimes, a barium pill is used to check for blockages.
4. Esophageal Manometry
- Measures muscle contractions and pressure in the esophagus when swallowing.
- Helps diagnose weak or uncoordinated esophageal muscles, which can contribute to GERD.
5. Transnasal Esophagoscopy (TNE)
- A thin, camera-equipped tube is inserted through the nose (instead of the mouth) to examine the esophagus.
- Less invasive than traditional endoscopy and doesn’t require sedation.
Treatments
1. First-Line Treatments (Lifestyle + Over-the-Counter Meds)
- Lifestyle changes: Avoid trigger foods, eat smaller meals, don’t lie down after eating, elevate your bed, and lose weight if needed.
- Antacids (Tums, Rolaids): Quick relief but don’t heal esophagus damage. Overuse can cause side effects.
- H2 Blockers (Pepcid, Tagamet): Reduce acid for up to 12 hours. Slower but longer-lasting than antacids.
- PPIs (Prilosec, Nexium): Stronger acid blockers that help heal the esophagus. Available OTC or by prescription.
2. Prescription Medications
- Stronger PPIs (Protonix, Dexilant): For severe GERD. Long-term use may cause side effects (headaches, low B12/magnesium).
- Prescription H2 Blockers: Higher-dose famotidine/nizatidine for persistent symptoms.
3. Surgery (If Meds Don’t Work or Long-Term Use Isn’t Ideal)
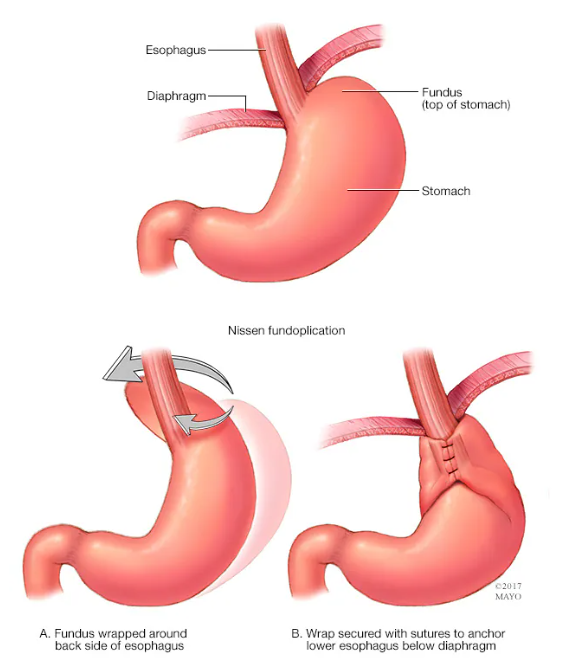
- Fundoplication: The Stomach is wrapped around the esophagus to strengthen the valve (minimally invasive). (🔗)
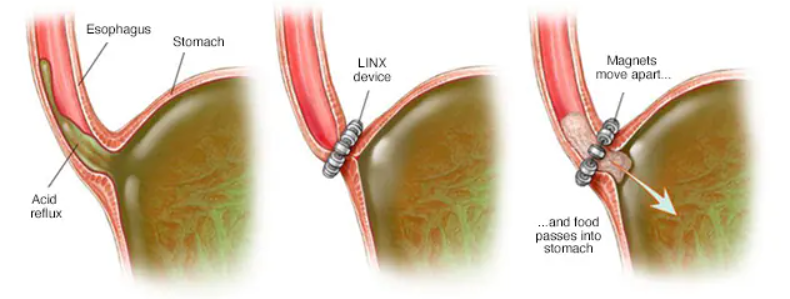
- LINX Device: Magnetic beads placed around the esophagus to prevent reflux but allow food to pass.
- TIF (Incisionless Procedure): Endoscopic tightening of the esophagus valve—faster recovery, no incisions.
- Weight Loss Surgery: Recommended if obesity worsens GERD.
What causes Acid Reflux?
At the core of GERD is a malfunctioning lower esophageal sphincter (LES)—the muscular valve separating your esophagus from your stomach. Normally, the LES opens only to let food down or allow gas out (like during burping). But if it weakens or relaxes abnormally, stomach acid can splash back up, causing reflux.
Hiatal Hernia
Part of the stomach bulges through the diaphragm into the chest, displacing the LES. This traps acid near the esophagus and reduces the LES’s ability to stay closed. More common with age and a major contributor to chronic GERD.
Pregnancy
Hormones (progesterone, estrogen, and relaxin) loosen the LES. A growing uterus increases abdominal pressure, pushing acid upward. Usually temporary but can trigger long-term issues.
Obesity
Excess belly fat raises abdominal pressure, straining the LES. Fat tissue produces estrogen, which may further relax the valve. Linked to hiatal hernias and permanent LES weakening.
Smoking
Chemicals in tobacco directly relax the LES. Coughing fits force the valve open, allowing acid to escape. Slows digestion and increases stomach acid production.
Other Less Common Causes:
- Birth defects (e.g., esophageal abnormalities).
- Connective tissue disorders (e.g. scleroderma) that weaken esophageal muscles.
- Surgery or scarring near the esophagus.
- Medications like blood pressure drugs, sedatives, NSAIDs, or asthma meds that relax the LES.
Can foods cause acid reflux?
Foods and drinks probably aren’t enough to cause acid reflux alone, but they can contribute to it. Chocolate, coffee, alcohol, mint, garlic, and onions may have a relaxing effect on your LES in higher doses.
Fatty foods increase stomach acid and take longer to digest, so there’s more opportunity for acid to escape. If you have a heavier meal for dinner, it might not have time to digest before you lie down.
What health problems can persistent GERD lead to over time?
Stomach acid is highly corrosive—designed to break down food, but harmful to other organs. While your stomach has a protective lining, your esophagus, throat, and airways don’t. Repeated acid exposure can lead to serious complications:
- Esophagitis – Chronic inflammation damages the esophageal lining, causing pain, ulcers, and scarring. Over time, this may trigger abnormal tissue changes.
- Barrett’s Esophagus – In response to long-term acid exposure, the esophagus lining can transform into intestinal-like tissue. This precancerous condition increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Esophageal Stricture – Scar tissue from repeated injury can narrow the esophagus, making swallowing difficult and affecting nutrition.
- Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) – When acid reaches the throat, it can cause hoarseness, vocal cord damage, and breathing issues. At night, acid may even be inhaled into the lungs.
- Asthma & Respiratory Problems – Acid particles irritating the airways can worsen asthma or trigger chronic coughing, wheezing, and breathing difficulties.
Why It Matters: Without treatment, GERD doesn’t just cause discomfort—it can lead to permanent damage and serious health risks. Early management is key to preventing complications.

What should I anticipate if I’m experiencing Acid Reflux?
Acid reflux can stem from multiple factors, making the exact cause tricky to pinpoint. While lifestyle changes often help mild cases, conditions like hiatal hernias may worsen over time.
Treatment depends on severity:
- Mild reflux? Home remedies and diet adjustments may suffice.
- Frequent or severe symptoms? Prescription medications can provide relief for most people.
Why see a doctor? Even occasional reflux should be evaluated—it could signal hidden complications.
When is surgery needed? If medications fail or complications arise, minimally invasive procedures can effectively restore normal function.
How to Relieve Acid Reflux Naturally at Home
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals: Large meals stretch the stomach, increasing pressure on the LES (the valve that keeps acid down).
- Finish dinner 3+ hours before bed: Lying down too soon after eating makes it easier for acid to escape.
- Avoid trigger foods: Spicy, fatty, acidic, or fried foods can worsen reflux.
- Sleep on your left side: This keeps the LES above stomach acid, reducing nighttime reflux.
- Elevate your head 6-8 inches: Uses gravity to keep acid in your stomach.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing: Tight waistbands squeeze the stomach, forcing acid upward.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess belly fat increases abdominal pressure, weakening the LES over time.
- Tobacco relaxes the LES and increases stomach acid.
- Alcohol irritates the esophagus and triggers reflux.
- Antacids (Tums, Rolaids): Neutralize stomach acid quickly.
- Alginate drugs (Gaviscon): Form a protective barrier to block reflux.
FAQS
FAQ 1: Can Untreated GERD Cause Serious Health Problems?
Chronic GERD can damage your esophagus over time, leading to conditions like esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus (a precancerous change), and esophageal strictures. Acid reflux can also affect your lungs and throat, potentially causing chronic cough, asthma flare-ups, or voice changes. Early treatment helps prevent these complications.
FAQ 2: How Do I Know If I Have GERD or Just Occasional Heartburn?
Occasional heartburn is common, but GERD is diagnosed when you experience acid reflux symptoms (like burning chest pain or regurgitation) at least twice a week for several weeks. If over-the-counter medications don’t help or symptoms disrupt your sleep/daily life, see a doctor for evaluation. Persistent GERD may require long-term management.